By Bridget K. Burke
Healthcare is no stranger to innovation; however, the speed at which artificial intelligence (AI) is advancing healthcare is unparalleled. Consider that OpenAI’s ChatGPT reached a staggering 1 million users within just 5 days of its launch in November 2022, shattering the previous average of 570 days needed for an app to reach the same milestone. This is a pace that we have never seen before in technology evolution (Table 1).
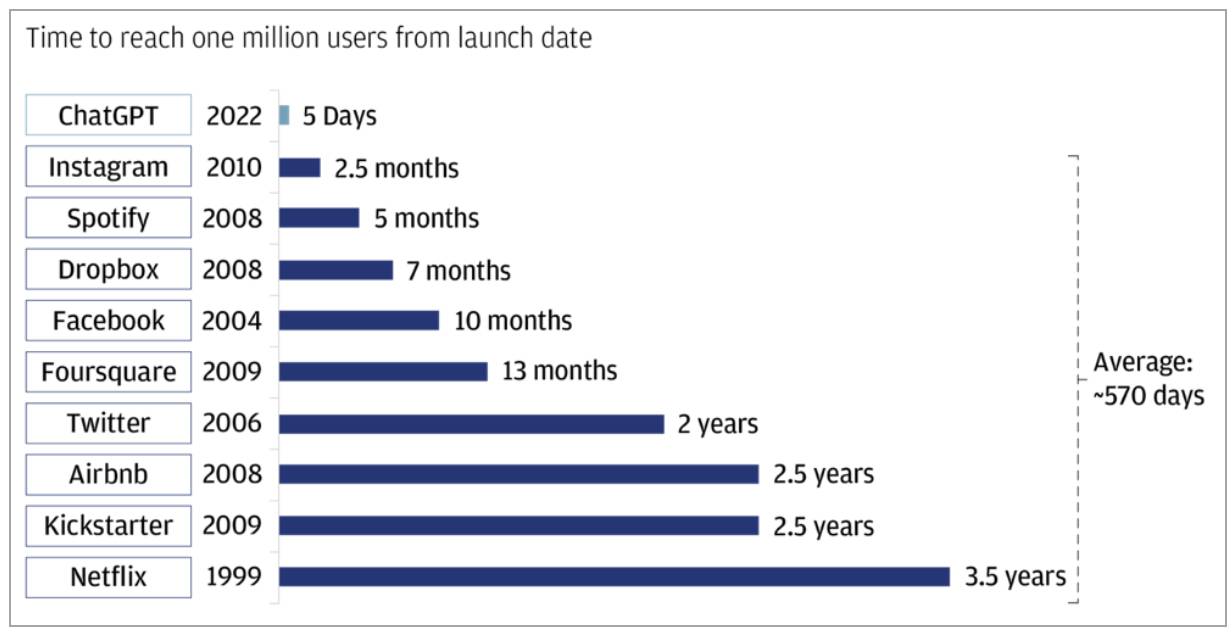
Table 1. Time to reach one million users from launch date, J.P. Morgan Private Bank, Statista.
While AI-based software is not new in healthcare, until recently, it wasn’t possible to run many of the algorithms: The computing power they require to learn and make predictions is massive. But that changed in 2021 with the advent of new fast hardware, high-speed storage, high-capacity networks, high power density racks, and liquid cooling systems. The new ability to run AI software algorithms on massive Large Language Model (LLM) datasets enabled the AI inflection point in 2022, with ChatGPT being the first to take advantage of the alignment. Healthcare is now feeling the pressure to evolve rapidly and adopt generative AI programs that promise a big shift in the ability to deliver clinician-centric, patient-focused, efficient healthcare.
Why should healthcare leaders care about AI?
AI is not just another entry in the technology evolution timeline. The rate at which AI technologies like ChatGPT have been adopted eclipses prior technology major milestones in electrification, telecommunications, computing, and genomics. These earlier technologies took years or even decades to become pervasive. In the AI era, the adoption timeline has shrunk from decades to days. Yes, days (Figure 1).
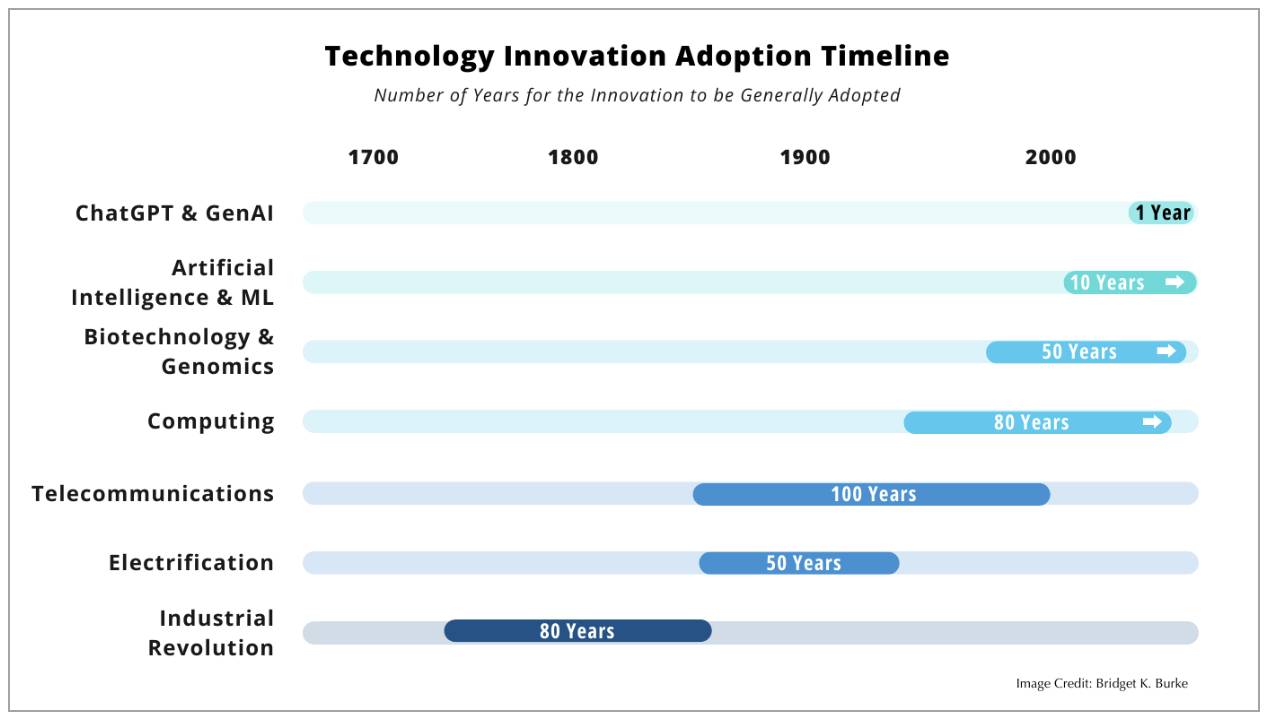
Figure 1. Technology innovation adoption timeline
In less than one year since ChatGPT’s launch, AI is being integrated into many aspects of healthcare. Healthcare tends to be conservative because it is concerned with not doing harm. On the other hand, innovation can improve patient outcomes and lower costs. Thus, medicine must maintain a delicate balance between too little and too much change. Although AI programs are proliferating, their adoption speed depends on the programs’ credibility and utility.
AI Competitive Landscape and Potential for Healthcare Integration
In healthcare, the value of any AI solution depends on its ability to either resolve existing or anticipate future challenges. Several emerging AI technologies could have a significant impact on the healthcare sector in the coming year. Let’s look at some of the biggest AI development companies; Amazon, Google, Microsoft, OpenAI, and Oracle, and their major AI announcements in the past 45 days that are shaping the AI landscape in healthcare today (Table 2).
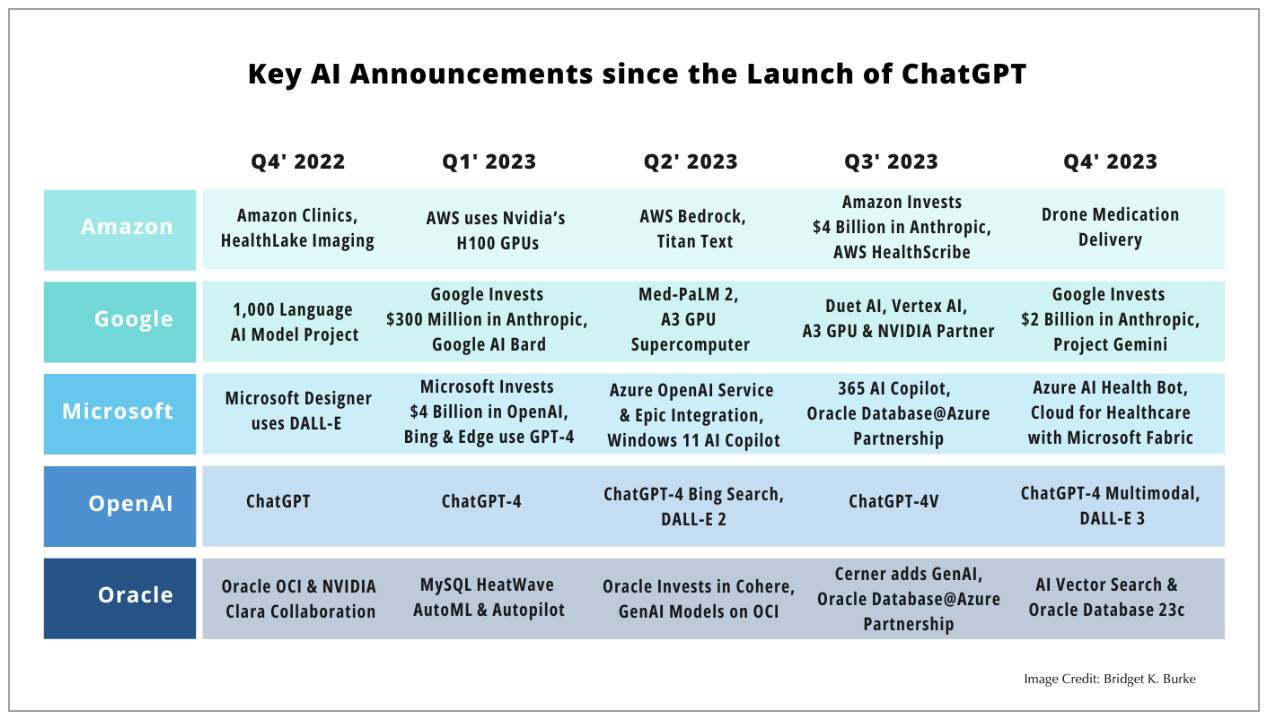
Table 2. Key AI announcements from Amazon, Google, Microsoft, OpenAI, Oracle since the launch of ChatGPT
Amazon and Anthropic: A Generative AI Collaboration with EHR Implications
Amazon recently announced an investment commitment of up to $4 billion in Anthropic. Amazon Web Services (AWS) will integrate Anthropic’s AI models like Claude2, known for their safety and large-scale generative capabilities, into AWS. AWS will become Anthropic’s primary cloud provider for critical workloads.
With the partnership, healthcare systems already on AWS will be able to combine Anthropic models with their existing healthcare LLMs and potentially integrate it with their Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems to summarize lengthy patient histories, assist in intricate medical research by automating large dataset analysis, crucial in drug discovery and epidemiological studies, streamlining clinical decision support by analyzing extensive patient data in real-time for data-driven insights, enhancing diagnostic algorithms for early disease detection, and personalized treatment plans tailored to an individual genetic and environmental factors as well as streamlining operational tasks like automated medical coding and billing, and enhancing accuracy and compliance.
Amazon’s commitment to using high-performance, low-cost machine learning solutions has the potential to provide a competitive and cost-effective solution comparable to similar products and partnerships in the market. The Amazon-Anthropic collaboration competes with other cloud and AI services. Still, with Amazon’s extensive experience in cloud computing, combined with Anthropic’s expertise in safer and advanced generative AI, the partnership might offer superior safety features – a potential competitive advantage in the sensitive healthcare sector.
Google’s Generative AI Focus
Google’s recent advancements in AI will have a substantial impact on healthcare. The latest release of Google’s Medical Language Model 2 (Med-PaLM 2), a medically-tuned LLM designed to provide high-quality answers to medical questions, it can retrieve medical knowledge, accurately answer medical questions, and provide reasoning, it is targeted to the healthcare and life sciences sectors. Recently, it achieved a remarkable 86.5% accuracy on U.S. Medical License Exam (USMLE)-style questions. It has the ability to process and analyze multimodal data including medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, along with clinical data, patient histories, genetic information, and medical literature. Its insights into complex medical conditions are often more comprehensive and accurate than those of healthcare experts.
Google’s Project Gemini is a next-generation conversational, multimodal AI model that uses a set of LLMs and incorporates AlphaGo-inspired techniques with capabilities such as planning or solving problems. Its conversational AI capabilities can be used to create intuitive and user-friendly interfaces for electronic health records (EHR) systems or patient portals through chatbots, helping in appointment scheduling, personalized responses to patient inquiries, medication reminders, and providing general healthcare information in a conversational manner. Moreover, its integration into telemedicine platforms could bolster virtual care delivery, offering real-time support and personalized patient interactions.
Google’s investments in AI, especially in generative and conversational AI, provides a strong foundation for their Google Heath platform as it looks to position itself against competitors like Amazon and Microsoft.
Microsoft’s New AI Features
Microsoft recently announced several significant AI-powered innovations. Most notable is Microsoft Copilot, a natural language AI program that provides context-aware responses. It will be integrated within key products such as Windows 11, Bing, Edge, and Microsoft 365. Copilot is also being integrated with EHR systems like Epic to streamline clinical documentation by auto-generating reports from medical dictations and automating administrative tasks such as scheduling and billing. It will also aim to enhance clinical decision support by aiding physicians in accessing relevant data and predictive analytics, improve remote patient monitoring, personalize patient engagement for better adherence to treatment plans, enhance telemedicine services through virtual health assistants providing preliminary consultations, and enrich virtual consultations with real-time information.
The potential utility of Microsoft Copilot is high for enhancing productivity across various Microsoft applications. Additionally, within Microsoft 365, Copilot is designed to detect user job roles, priorities, and organizational structure and deliver personalized assistance, thereby potentially reducing the time and effort required in managing routine or complex tasks. Healthcare organizations already within Microsoft’s ecosystem will be able to leverage these features as of November 1, 2023 when it will be generally accessible to enterprise customers.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT Multimodal Generative AI Enhancements
OpenAI is an established pioneer in AI, with a track record of innovations and practical applications in healthcare. Their partnerships with Microsoft and Epic and collaboration with Hint Health to explore AI’s promise in healthcare indicate a practical application and trust in using OpenAI’s technology in healthcare.
OpenAI recently announced several enhancements to ChatGPT, introducing voice and image recognition (GPT-4V) capabilities, allowing users to have voice conversations and use images to ask questions. The voice technology is driven by a novel text-to-speech model capable of generating human-like audio, while image understanding is powered by the advanced multimodal GPT-4 model.
In healthcare, the new capabilities of ChatGPT have the potential to facilitate real-time discussions and interactive problem-solving, to develop chatbots for patient triage, to create virtual assistants to aid in medical imaging and treatment planning, to automate routine tasks such as customer service, to improve dictation of physician’s notes, and to enhance administrative duties like data entry and scheduling.
Their move to enrich ChatGPT with voice and image recognition is in line with a broader trend of AI platforms competing with virtual assistants and other AI services, aiming to provide a one-stop solution for AI needs. ChatGPT is positioned as a formidable player in the AI healthcare market, potentially offering a highly competitive, comprehensive, multimodal tool.
Oracle’s AI Vector Search
Oracle is a major player in enterprise database management systems. Their new AI Vector functionality is well positioned to compete in the expanding market of vector databases, alongside Microsoft and emerging players like Pinecone, Chroma DB, and Weaviate. Oracle’s introduction of its AI Vector Search in Oracle Database 23c and its integration into the Cerner EHR system is a significant step forward in utilizing generative AI for fast, precise semantic search on unstructured data such as documents and images. They have also incorporated Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), a new generative AI technique, that combines large language models with private business data for accurate and secure responses to natural language questions.
For healthcare, AI Vector Search could accelerate and refine operations and research endeavors. Its application promise includes automating anomaly detection in medical imaging, bolstering Clinical Decision Support Systems, enhancing real-time patient data monitoring, expediting drug discovery, and personalizing medicine. Oracle’s new AI database functionality stands out for its user-friendliness and low learning curve that requires no machine learning expertise. It has the potential to rapidly run similarity queries on vast amounts of unstructured data. This positions it as a valuable tool for healthcare organizations aiming to employ AI without using database/ML experts while also ensuring data security and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Oracle’s new integrated vector database 23c offers a unique blend of innovative AI functionality, user-friendliness, competitive pricing, and credibility, making it a leading-edge solution to consider in the evolving vector database management landscape as well as for healthcare organizations using the Oracle Cerner EHR platform.
Conclusion
The rapid evolution of AI in healthcare is both undeniable and unparalleled. Prominent players like Amazon, Anthropic, Google, Microsoft, OpenAI, and Oracle are not merely introducing novel technologies; they are reshaping the healthcare landscape. Each company brings unique capabilities that invite careful consideration from healthcare leaders. However, despite the transformative potential of these technologies, the adoption and integration of AI in healthcare are not without challenges. Healthcare leaders need to manage issues of data security, privacy, and the ethical use of AI while striking a balance between innovation and caution, ensuring that every AI adoption resonates with the core tenets of healthcare: safety, reliability, and patient-centricity. As AI reshapes healthcare it offers an invitation to healthcare leaders: to lead with vision, adapt with agility, foster a culture of continuous learning, maintain a diligent focus on ethical, responsible AI deployment, and above all, champion the cause of patient-centric care.

